A type S thermocouple (platinum—Platinum Rhodium-10%) is often applied in high-temperature applications, particularly in the Pharmaceutical and Biotech industries.
Its high stability and accuracy mean that it can also be used in low-temperature applications. A ceramic protection tube is normally used together with the type S thermocouple.
In terms of temperature range, this is what to expect from the type S thermocouple:
- Extension wire: 0 to 200®C (32 to 39®F)
- Thermocouple grade wire -50 to 1480®C
- Short term use: up to 1,700®C (3,092®F)
- Maximum continuous operating temperature: Up to 1,600®C (2,912®F)
Choosing a Thermocouple
Given that the thermocouple tends to take varying forms and shapes, users must have an idea of how to go about selecting the right sensor.
Some of the critical factors considered when making this decision include:
- The installation requirements
- Temperature range
- Vibration and abrasion resistance
- Chemical resistance
Installation requirements are critical in that they get to dictate a user’s preferred choice. Thermocouples come in varying forms, which means that their uses will also vary.
Exposed thermocouples are preferred and recommended in instances requiring high response times. Underground thermocouples are ideal for use in corrosive environments.
Certain considerations can assist you in choosing a suitable thermocouple. They include, but are not limited to, the following factors:
I. The application where you intend to use the thermocouple
II. The temperature ranges expected in the probe
III. The kind of response time needed
IV. The type of vibration, abrasion, or chemical resistance that may be encountered
V. The thermocouple installation requirements
The Inner Workings of a Thermocouple
A continuous current begins flowing in a thermoelectric circuit whenever two wires made from various metals get joined on both ends, and one of the ends gets heated.
The Seebeck voltage, also called the net open circuit voltage, is a composition of the two metals and a function of the junction temperature occurs when the circuit gets broken.
What this means is that a voltage gets produced whenever the two metals are cooled or heated. The resulting voltage can be related to a temperature.
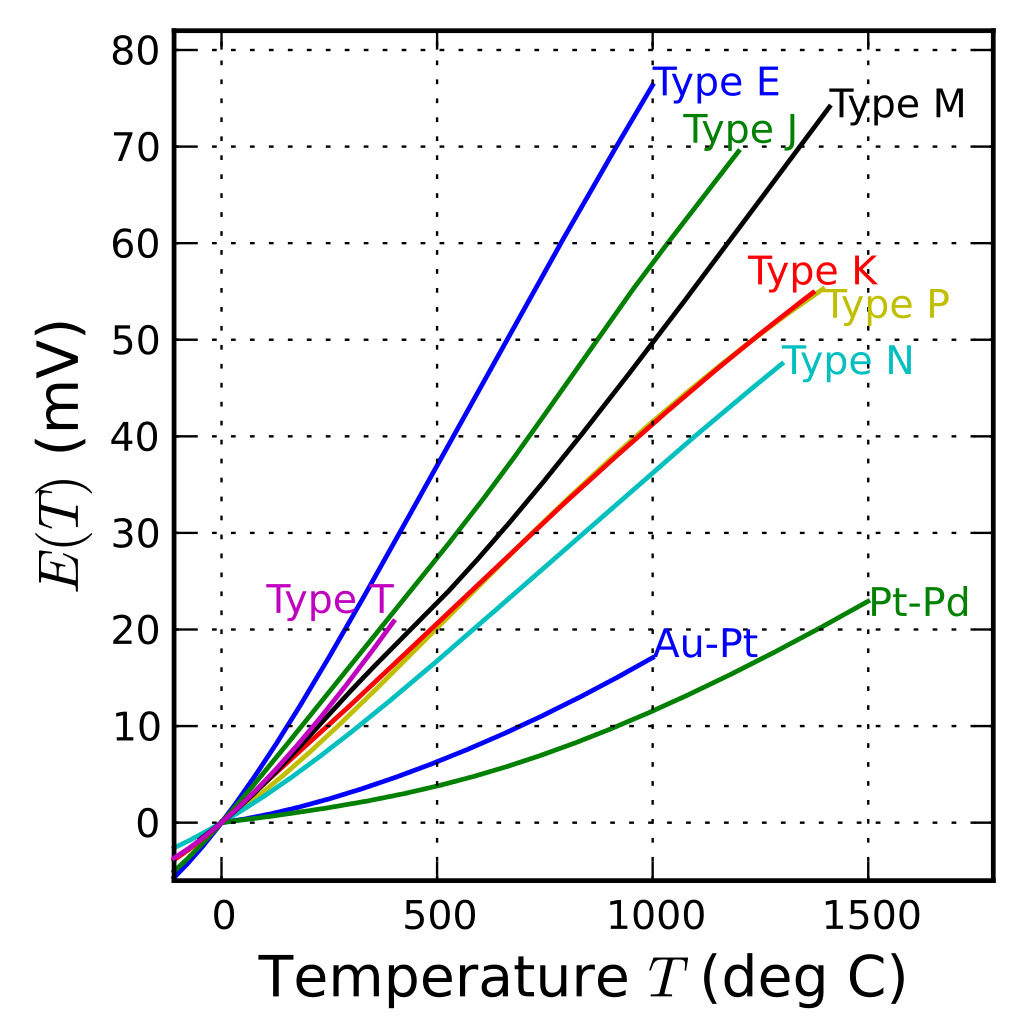
Thermocouple Wire vs. Thermocouple Probes
Thermocouples exist in varying blends, metal calibrations, or combinations. The Base metal thermocouples happen to be the most common.
They are referred to as Types N, J, E, T, and K. Furthermore, there also exists the Noble Metal thermocouples, sometimes referred to as the high-temperature calibrations.
Included in this group are the Types GB, R, C, and S.
Every available calibration comes with its own temperature environment and range, even though the diameter of the thermocouple wire determines the maximum temperature.
While calibration is the primary determinant of the temperature range, the thermocouple’s wire diameter can as well influence the maximum range.
A Type K thermocouple has a low-temperature range and is highly affordable, so it’s at times called the general purpose thermocouple.
The Life Expectancy of a Thermocouple
Experts recommend replacing the thermocouples every twelve to twenty-four months.
A Type K thermocouple’s life expectancy begins to drop drastically when the temperature scale goes above the recommended range of 1,200®F.
Elements subjected to a range of between 1,500® to 1,800®F begin to show deterioration signs within six to twelve months.
Determining If a Thermocouple is Functional
The main role of the thermocouple is to ensure the pilot will remain lit. It’s able to accomplish this by transmitting a small electric current to the sensor in your gas valve telling it to remain open.
As things stand, nothing lasts forever, which means that the thermocouple will at some point begin to wear out. It’s, however, essential to note that the pilot lit can stop functioning for several reasons.
In some cases, it may not be the thermocouple’s fault. However, when the thermocouple is at fault, you won’t have a way of determining whether the pilot light is burning.
Whenever a pilot light goes out, it means that you won’t have any hot water in the plumbing system. You can test whether the problem lies in the thermocouple by attempting to relight the pilot light.
Worn-out Thermocouples
Thermocouples do get worn out over time, but the good news is that they are easily replaceable.
Nevertheless, it’s highly recommended that one conducts several tests before they can replace the thermocouple.
The tests are meant to confirm that it’s the thermocouple at fault because there exist many reasons that could cause the gas pilot to go off unexpectedly.
During the tests, make sure also to test the thermopile. A thermopile is tasked with opening gas to the available burners.
Testing both devices will give you a better idea of what is causing the pilot light not to work. It also ensures you won’t end up buying a new thermocouple, yet the existing one is fully functional.
If you’re unsure of how to go about the tests, make sure to consult with a professional!
- Elevating Value: Mastering Property Management in Brooklyn’s Luxury Rental Market - January 22, 2026
- Smart Door Access Control: Securing the Future of Modern Business - October 13, 2025
- Demystifying Fuel Test Procedures and Standards - January 16, 2025




